// Hot Forging
Hot forging is a key traditional process in automobile parts manufacturing. Its key advantages include high strength, exceptional durability, precise dimensional accuracy, and the ability to produce components with complex shapes. Hot-forged parts are extensively applied in critical automotive systems, such as transmission, suspension, and engine systems, playing a direct role in enhancing vehicle performance, safety, and reliability.
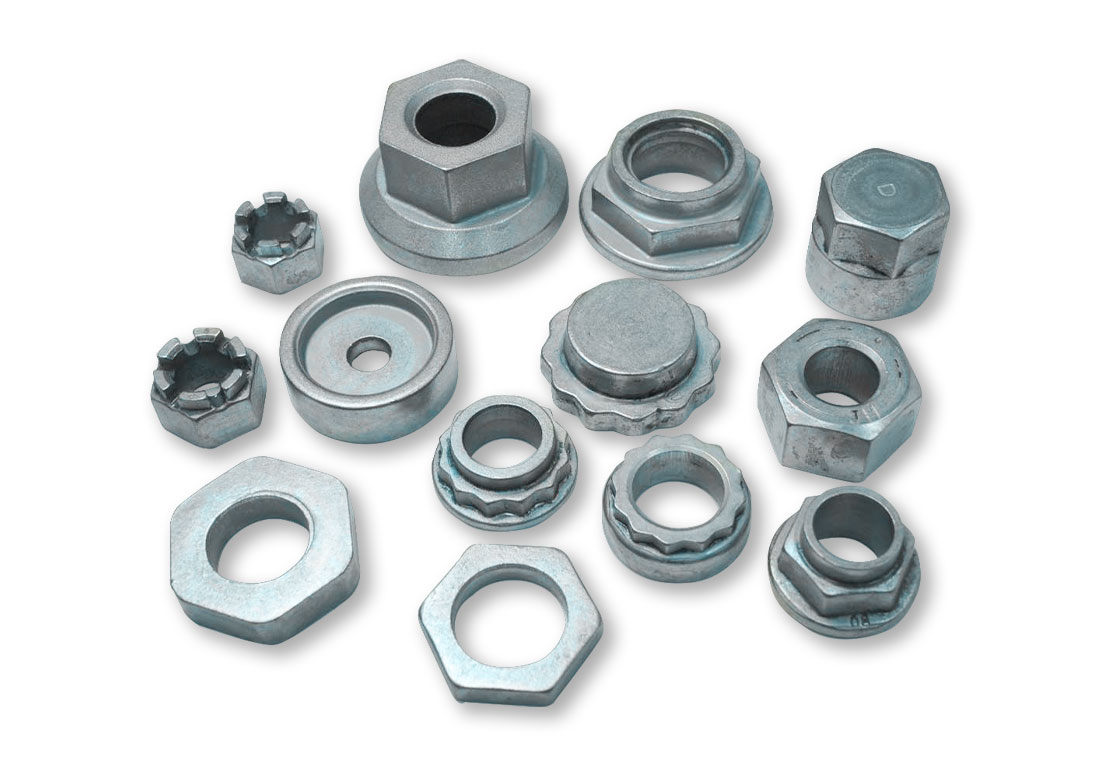
Hot Forged Parts – Blanks
The material for hot forging parts is forged using black oxide (mill scale) round bars, typically made of C1010 to C1050, 10B21 to 10B33, or SCM435 to SCM440.
Hot-forged blanks are relatively rough and usually undergo a shot blasting process before further machining.
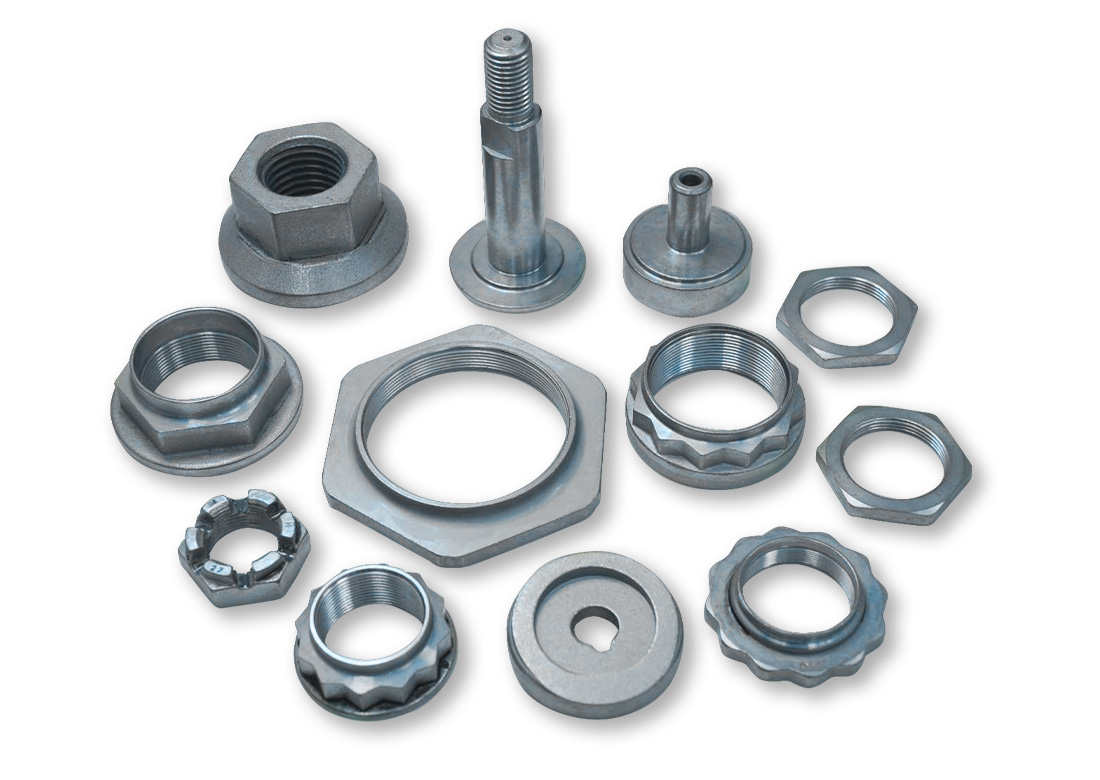
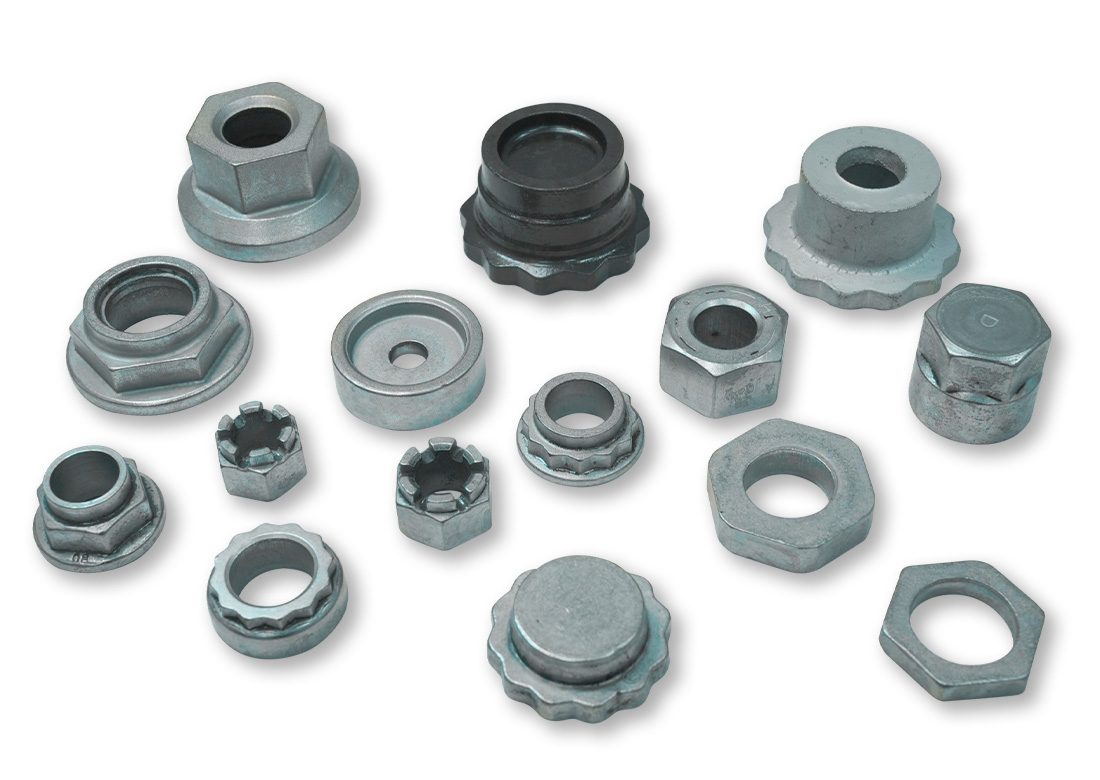
Hot Forged Parts – Finished Parts
The hot-forged blank becomes a finished product after subsequent processing, such as CNC turning or milling.
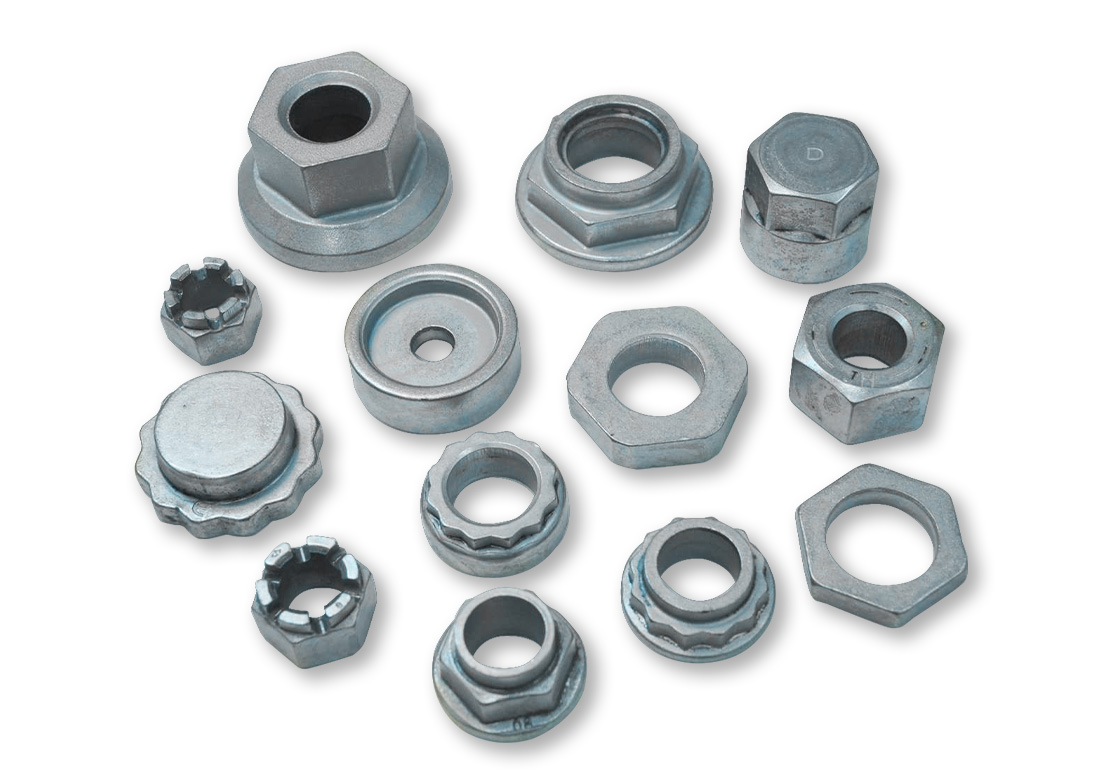
Hot Forged Parts – Blanks
The material for hot forging parts is forged using black oxide (mill scale) round bars, typically made of C1010 to C1050, 10B21 to 10B33, or SCM435 to SCM440.
Hot-forged blanks are relatively rough and usually undergo a shot blasting process before further machining.